Introdução às normas para guindastes à prova de explosão
Entendemos que selecionar a certificação à prova de explosão adequada para pontes rolantes e talhas é fundamental para a segurança operacional em ambientes perigosos. Como líder no setor, fabricante de guindastes industriais Com décadas de experiência atendendo mercados globais, reconhecemos que a conformidade com as normas corretas de proteção contra explosões não é meramente regulatória — é fundamental para proteger pessoas, ativos e produtividade. Este guia abrangente examina os três principais sistemas de certificação de equipamentos à prova de explosão: ATEX (europeu), IECEx (internacional) e GB (chinês), fornecendo comparações técnicas detalhadas para auxiliar no processo de seleção de equipamentos.
Entendendo os Fundamentos da Certificação à Prova de Explosão
A certificação à prova de explosão representa uma abordagem sistemática para o projeto de equipamentos que previne a ignição em atmosferas perigosas contendo gases inflamáveis, vapores ou poeira combustível. Essas normas exigem controles de engenharia específicos, seleção de materiais e protocolos de teste para garantir que os componentes elétricos e mecânicos não possam gerar faíscas, arcos elétricos ou temperaturas excessivas que possam desencadear explosões. pontes rolantes Em guindastes que operam em setores como processamento químico, petróleo e gás, mineração e fabricação farmacêutica, o cumprimento dessas normas é imprescindível para a segurança operacional.
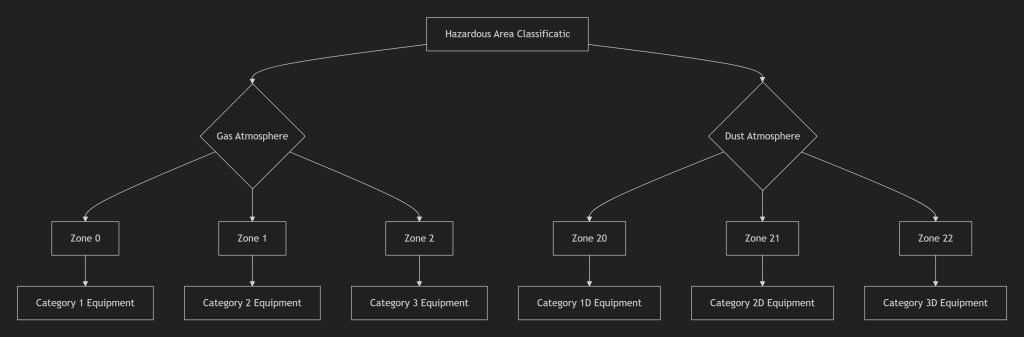
Sistemas de Classificação de Áreas Perigosas
Zona 0: Atmosfera explosiva presente continuamente ou por longos períodos. Zona 1: Atmosfera explosiva provável durante operações normais. Zona 2: Atmosfera explosiva improvável em condições normais.
Zona 20: Presença contínua de poeira combustível Zona 21: Possibilidade de poeira combustível durante operações normais. Zona 22: Poeira combustível improvável em condições normais.
Normas ATEX: Diretiva Europeia 2014/34/UE
Quadro regulatório e âmbito de aplicação

Categorias de equipamentos e níveis de proteção
Métodos de proteção: Ex ia (segurança intrínseca), Ex ma (encapsulamento) Fatores de segurança exigidos: redundância dupla ou medidas de segurança reforçadas
Métodos de proteção: Ex d (à prova de explosão), Ex e (segurança aumentada), Ex ib (segurança intrínseca) Documentação completa, incluindo arquivo técnico de construção.
Métodos de proteção: Ex n (sem faíscas), Ex ec (segurança aumentada) Procedimento simplificado de avaliação da conformidade
Processo de Certificação ATEX
Testes de aumento de temperatura para verificar se as temperaturas da superfície permanecem abaixo dos pontos de ignição. Testes de impacto para garantir a integridade da caixa sob tensão mecânica. Teste de proteção contra ingresso (mínimo IP54 para equipamentos elétricos) Teste de ignição por faísca para materiais não metálicos
Certificação IECEx: Normalização Internacional
Reconhecimento e aceitação global

Requisitos técnicos principais
Grupo I: Aplicações de mineração (ambientes com metano) Grupo II: Indústrias de superfície (diversas classificações de gás)
T1: 450 °C máximo T6: 85°C máximo (mais rigoroso)
IIC: Hidrogênio, acetileno (mais volátil) IIB: Etileno IIA: Propano
Vantagens da Certificação IECEx
O sistema IECEx oferece vantagens significativas para operações internacionais: Certificação única aceita em vários países. Requisitos de documentação simplificados através do Sistema de Avaliação de Qualidade IECEx Redução das redundâncias nos testes por meio de acordos de reconhecimento mútuo. Certificação integrada de competências de pessoal (Certificação IECEx de Competências de Pessoal)
Normas GB: Quadro Regulatório da China
Visão geral das normas nacionais chinesas

Sistema de Classificação Padrão GB
Ga/Da: Proteção muito alta (equivalente à Zona 0/20) Gb/Db: Alta proteção (equivalente à Zona 1/21) Gc/Dc: Proteção reforçada (equivalente à Zona 2/22)
Símbolo Ex Tipo de proteção (d, e, i, etc.) Categoria de equipamento (I, II, III) Classe de temperatura Nível de proteção do equipamento
Processo de Certificação GB
Testes de tipo realizados por laboratórios chineses designados Auditorias de fábrica realizadas por inspetores aprovados pela SAMR. Testes de amostra para cada categoria de produto Auditorias de acompanhamento anuais para manter a certificação.
Análise comparativa: normas ATEX vs IECEx vs GB
Aplicabilidade geográfica e acesso ao mercado
| Aspecto | ATEX (UE) | IECEx (Global) | Padrões GB da China |
|---|---|---|---|
| Escopo | Aplica-se a equipamentos utilizados em atmosferas potencialmente explosivas na União Europeia. | Sistema de certificação internacional reconhecido em mais de 30 países em todo o mundo. | Norma nacional para equipamentos à prova de explosão utilizados nas indústrias nacionais da China. |
| Autoridade Reguladora | Comissão Europeia e Organismos Notificados autorizados. | Comissão Eletrotécnica Internacional (IEC) por meio de Organismos de Certificação aprovados (ExCBs). | Administração Estatal de Regulação de Mercado (SAMR) e Centro de Certificação CNEx. |
| Classificação de Áreas Perigosas | Zonas 0, 1, 2 (Gases); Zonas 20, 21, 22 (Poeiras). | Zonas 0, 1, 2 (Gases); Zonas 20, 21, 22 (Poeiras). | Zonas 0, 1, 2 (Gases); Zonas 20, 21, 22 (Poeiras). |
| Métodos de proteção | Ex d (À prova de chamas), Ex i (Segurança intrínseca), Ex e (Segurança aumentada), Ex m, Ex t. | Ex d, Ex i, Ex e, Ex m, Ex tb (à prova de poeira), Ex p (pressurização). | Ex d, Ex i, Ex e, Ex n — adaptados para condições de umidade e alta temperatura. |
| Processo de Certificação | Testes realizados por organismos notificados da UE; marcação CE e “Ex” obrigatórias. | Testado por laboratórios aprovados pela IECEx; Certificado de Conformidade IECEx emitido. | Testes realizados por laboratórios chineses autorizados; certificação CNEx obrigatória. |
| Reconhecimento | Válido em toda a UE; reconhecimento parcial internacional. | Reconhecido globalmente em todas as economias membros sem necessidade de novos testes. | Obrigatório na China; reconhecimento limitado fora da China. |
| Certificação de Pessoal | Não é exigido pela ATEX. | Requisito do Esquema de Competências de Pessoal da IECEx (IECEx 05). | Não é obrigatório; foca-se na certificação do produto. |
| Exemplo de marcação | Ex II 2G IIB T4 (para atmosferas gasosas). | Ex d IIC T4 Gb (para conformidade global). | Ex d IIC T4 Gb (certificado pela CNEx para uso na China). |
| Indústrias Primárias | Indústrias de petróleo e gás, química, marítima e de energia na UE. | Projetos globais de mineração, energia e petroquímica. | Refinarias, mineração, siderurgia e indústria manufatureira na China. |
Quadro regulatório e âmbito de aplicação
Comparação de Requisitos Técnicos
Cronograma e considerações de custo para certificação
Duração típica: 8 a 12 semanas Fatores de custo: taxas do Organismo Notificado, preparação da documentação técnica Vantagem competitiva: essencial para o acesso ao mercado da UE.
Duração típica: 6 a 10 semanas Fatores de custo: taxas de laboratório para testes, documentação internacional. Vantagem de mercado: Aceitação global simplificada
Duração típica: 10 a 16 semanas Fatores de custo: Requisitos de testes locais, serviços de tradução Vantagem competitiva: Essencial para entrar no mercado chinês.
Critérios de seleção para guindastes à prova de explosão
Avaliação do Ambiente Operacional
Substâncias inflamáveis específicas presentes (classificação do grupo de gases) Propriedades e níveis de concentração da poeira Fatores ambientais (temperatura, umidade, potencial de corrosão)
Parâmetros operacionais
Ciclo de trabalho e frequência de utilização do guindaste Acesso e intervalos de manutenção Protocolos de resposta a emergências e rotas de evacuação
Requisitos de Conformidade Regulatória
- Regulamentos locais:O cumprimento obrigatório das normas regionais no local onde o equipamento será instalado.
- Expansão futura:Territórios operacionais previstos que exigem certificações adicionais
- Requisitos específicos do setor:Regulamentações específicas do setor (por exemplo, petróleo, química, farmacêutica)
Fatores de compatibilidade técnica
- Sistemas Elétricos:Compatibilidade de tensão, frequência e sistema de proteção
- Interfaces de controle:Integração com sistemas de automação e segurança existentes
- Dimensões físicas:Restrições espaciais e requisitos de instalação
Integração em aplicações reais de guindastes
Guindastes à prova de explosão são indispensáveis em diversos setores, tais como:
refinarias petroquímicas (ATEX): Guindastes de viga dupla de 50 toneladas movimentam reatores pressurizados.
Operações de mineração (IECEx): Guinchos subterrâneos com controles Ex i gerenciam poços carregados de metano.
Usinas de aço e cimento (GB): Pontes rolantes com proteção contra poeira Ex tb garantem o manuseio seguro de materiais a granel.
Os sistemas comprovados em campo da KRC — como o seu Pontes rolantes de estilo europeu e guinchos industriais personalizados—são adaptáveis a qualquer ambiente perigoso, garantindo conformidade global e confiabilidade operacional.
Tendências futuras em normas à prova de explosão
Iniciativas de Harmonização
Organizações internacionais de padronização estão trabalhando para uma maior harmonização entre as normas ATEX, IECEx e GB. Participamos ativamente dessas iniciativas por meio de grupos de trabalho do setor, garantindo que nossos projetos de equipamentos antecipem os requisitos regulamentares em constante evolução. Organização Internacional de Normalização A ISO publica regularmente normas de segurança atualizadas relevantes para fabricantes de guindastes.